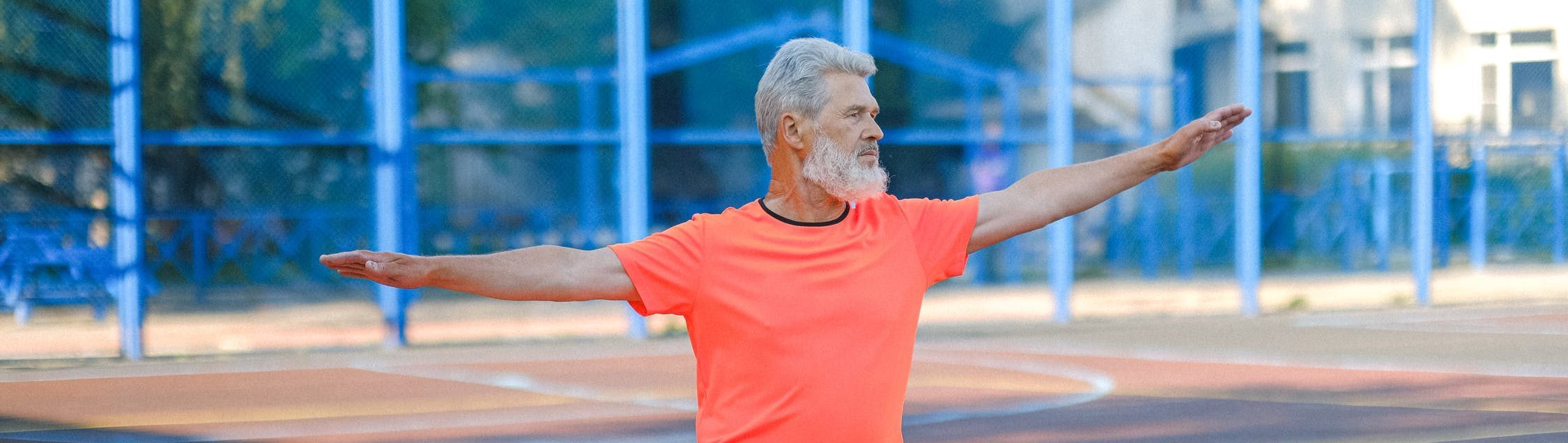

Ageing, Exercise, Recovery and Ubiquinol
Jun 2021Recent Article
As we grow older it is natural for our body’s Ubiquinol levels to decline which in turn may affect how we perform physically [1]. After age 30, our bodies’ natural Ubiquinol levels begin to deplete. Consistent and regular exercise may have a great effect on one’s health, however, as we age our body begins to feel the impact of this type of movement.
A clinical trial following 100 young and healthy German Olympic athletes found that taking a Ubiquinol supplementation regularly over a 6-week period significantly enhanced their peak physical performance by up to 11%.[2]
The same study suggested that Ubiquinol supplementation may have broader benefits beyond the realm of elite competitive sport. Meaning that everyday people, both young and elderly, may also experience an improvement in their physical performance from taking ubiquinol.
As we burn energy during physical activity, our body produces molecules with unpaired electrons (known as free radicals or ROS in scientific speak) which may interfere with the body tissue function. This may lead to oxidative stress, which in turn may accelerate health problems. Excessive physical exertion may produce potentially damaging oxidants during and after exertion, and as it is the role of antioxidants, including ubiquinol, found naturally in the body to combat these oxidants (free radicals) to help reduce oxidative stress. During and after this intense physical exertion it may become harder to exercise without feeling as though you are putting your body through excessive physical strain [3].
Ubiquinol, which is the active form of CoQ10, helps to support cellular energy production levels, which includes the cells found in the heart and the muscles [4]. Thus it becomes apparent as to why the depletion of energy in these areas may affect physical performance.
If feeling low on energy has been a leading reason as to why you have not been exercising consistently, you may wish to consider supplementing with ubiquinol, along with a healthy diet and lifestyle. Ubiquinol has many health benefits, including supporting heart health, supporting cellular energy productions, supporting fertility, reducing the impact of oxidative stress and helping support overall health and wellbeing.
Seek advice from a healthcare practitioner to determine if supplementation is right for you. Always read the label.
[1] Linnane, A. W., Zhang, C., Yarovaya, N., Kopsidas, G., Kovalenko, S., Papakostopoulos, P., … & Richardson, M. (2002). Human aging and global function of coenzyme Q10. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 959(1), 396-411. <https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02110.>
[2] [1] Alf, D., Schmidt, M.E. & Siebrecht, S.C. Ubiquinol supplementation enhances peak power production in trained athletes: a double-blind, placebo controlled study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 10, 24 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-10-24
[3] Tian, G, Sawashita, Kubo, H, Nishio, S, Hashimoto, S, Suzuki, N,Yoshimura, H, Tsuruoka, M, Wang, Y, Liu, Y, Luo, H, Xu, Z, Mori, M, Mitsuaki, K, Hosoe, K, Takeda, T, Usami, S, Higuchi, K. (2014). Ubiquinol-10 Supplementation Activates Mitochondria Functions to Decelerate Senescence in Senescence-Accelerated Mice. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 20(16):2606-20 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5406[4] Mendelsohn, B. A., Bennett, N. K., Darch, M. A., Yu, K., Nguyen, M. K., Pucciarelli, D., … & Nakamura, K. (2018). A high-throughput screen of real-time ATP levels in individual cells reveals mechanisms of energy failure. PLoS biology, 16(8), e2004624. <https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.2004624>
You can share this by:
Keep up-to-date with Ubiquinol News
Ubiquinol Headlines
Retail Pharmacy: Healthy Ageing in the Spotlight
Apr 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, APP, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Immunity, In The News, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Online, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Retail Pharmacy: The Impact of Loneliness on Heart Health
Apr 2025Category: cardiovascular health, dr ross walker, Heart, In The News, Mitochondrial health, Online, UbiquinolRead More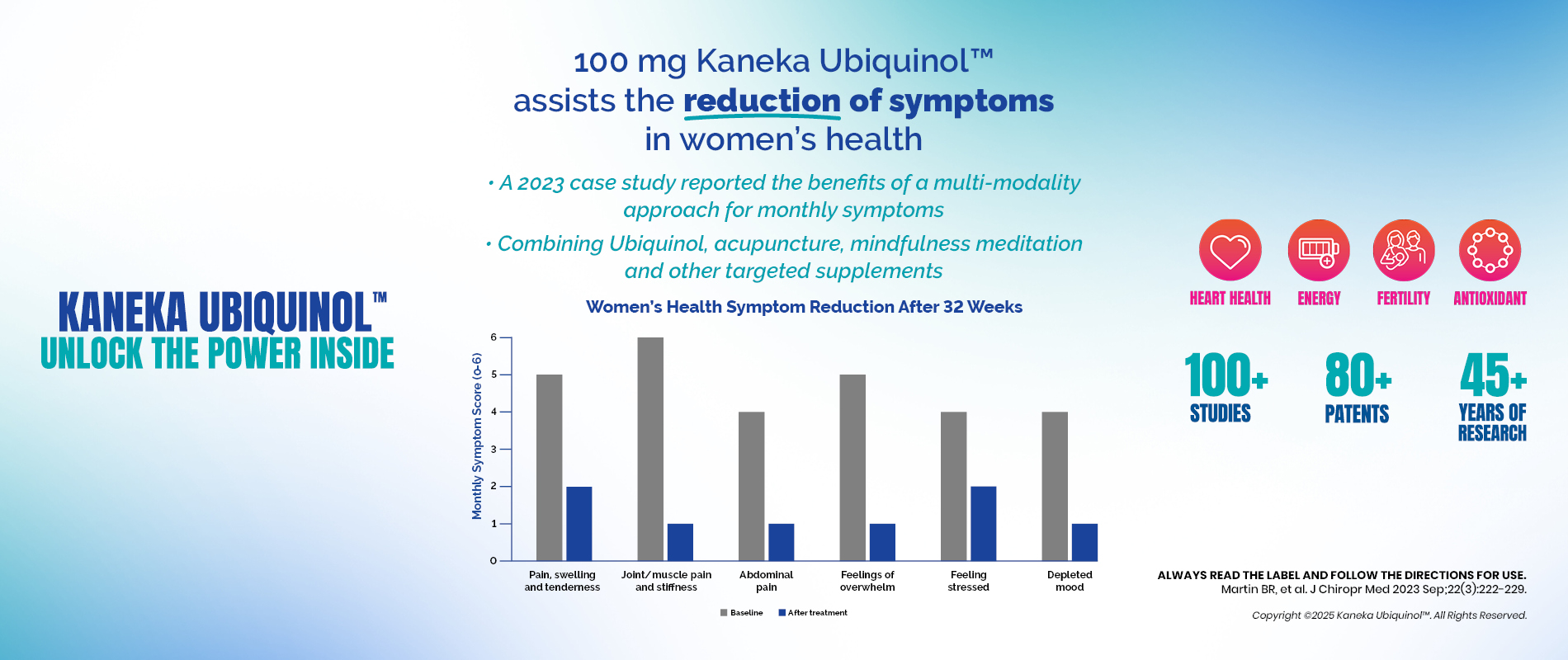
Ubiquinol for Women’s Health
Apr 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Fertility, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Ubiquinol, wellness, Women's HealthRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at APP 2025: Advancing Healthy Ageing & Longevity
Mar 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, APP, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, UbiquinolRead More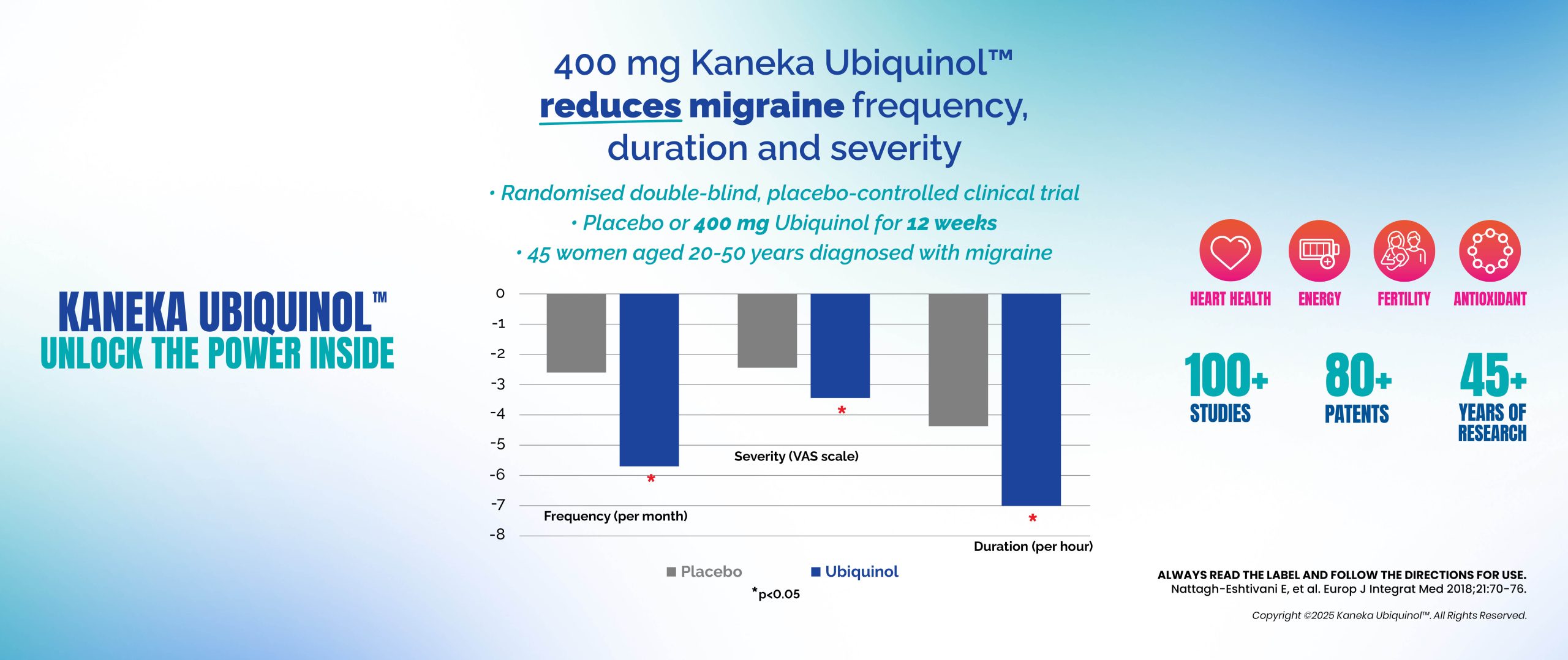
Ubiquinol: Supporting Migraine Relief Through Cellular Energy
Jan 2025Category: Antioxidants, complementary medicine, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at Functional Foods for Wellness Industry Awards and Summit, #FFWS2025
Jan 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, FFWS2025, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol Wins Prestigious Complementary Medicines Raw Material Supplier of the Year Award 2024
Dec 2024Category: Ageing, Awards, cardiovascular health, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, Lungs, Memory, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Online, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More

