
How to Support Mitochondrial Health
Jul 2021Recent Article
The mitochondria is often referred to as the powerhouse in each one of the trillions of cells found inside of our bodies.
The mitochondria are responsible for producing energy (in the form of Adenosine triphosphate or ATP) for optimal cell, and therefore tissue, performance. Therefore, it is clear that mitochondrial health is critical in ensuring and maintaining optimal energy levels and health.
There are two easy ways you can support your mitochondrial health naturally:
Exercise and movement
We are all aware that there are many benefits to being active and maintaining a regular exercise routine for our overall health and wellbeing. Regular exercise also supports our Mitochondria to function at an optimal level too. Our muscles have the highest mitochondria count of any tissue in the body, with research showing that higher levels of mitochondria in the muscles could be linked to better health[1].
A new study found that exercise in particular high-intensity interval training in aerobic exercises such as riding a bike and brisk walking can help the cells to make more proteins for their mitochondria that will be used in different cellular processes including the production of ATP[2].
So when we train and move our bodies in particularly high-intensity intervals, we are increasing the mitochondrial content per gram of tissue improving its ability to produce energy[3].
Fuel your mitochondria
Our mitochondria requires the right fuel to carry out its core purpose and functions.
Ubiquinol, the active form of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), is a fat-soluble antioxidant found naturally in the body that supports cellular energy production by assisting the synthesis of ATP in the mitochondria. Optimal levels of Ubiquinol have been shown to support optimal mitochondrial health[4].
Ubiquinol can also be found in certain foods like oily fish, organ meats and whole grains. However, it is difficult to achieve the daily recommended dose without consuming excessive amounts of these foods as you would need to consume more than 14kg of sardines or 60 avocados, for example, to reach 100 mg of Ubiquinol.
Taking Ubiquinol in a supplement form can ensure you easily achieve the recommended daily dose. Seek advice from a healthcare practitioner to determine if supplementation is right for you. Always read the label.
[1] Menshikova, E., Ritov, V., Fairfull, L., Ferrell, R., Kelley, D. and Goodpaster, B., 2006. Effects of Exercise on Mitochondrial Content and Function in Aging Human Skeletal Muscle. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, [online] 61(6), pp.534-540. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1540458/ [Accessed 4 August 2021].
[2] Cell Press. 2017. How exercise — interval training in particular — helps your mitochondria stave off old age.. [online] Available at: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/03/170307155214.htm [Accessed 4 August 2021].
[3] Jesus R. Huertas, Rafael A. Casuso, Pablo Hernansanz Agustín, Sara Cogliati, “Stay Fit, Stay Young: Mitochondria in Movement: The Role of Exercise in the New Mitochondrial Paradigm”, Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, vol. 2019, Article ID 7058350, 18 pages, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7058350
[4] Neergheen, V., Chalasani, A., Wainwright, L., Yubero, D., Montero, R., Artuch, R. and Hargreaves, I., 2017. Coenzyme Q10 in the Treatment of Mitochondrial Disease. Journal of Inborn Errors of Metabolism and Screening, 5, p.232640981770777.
You can share this by:
Keep up-to-date with Ubiquinol News
Ubiquinol Headlines
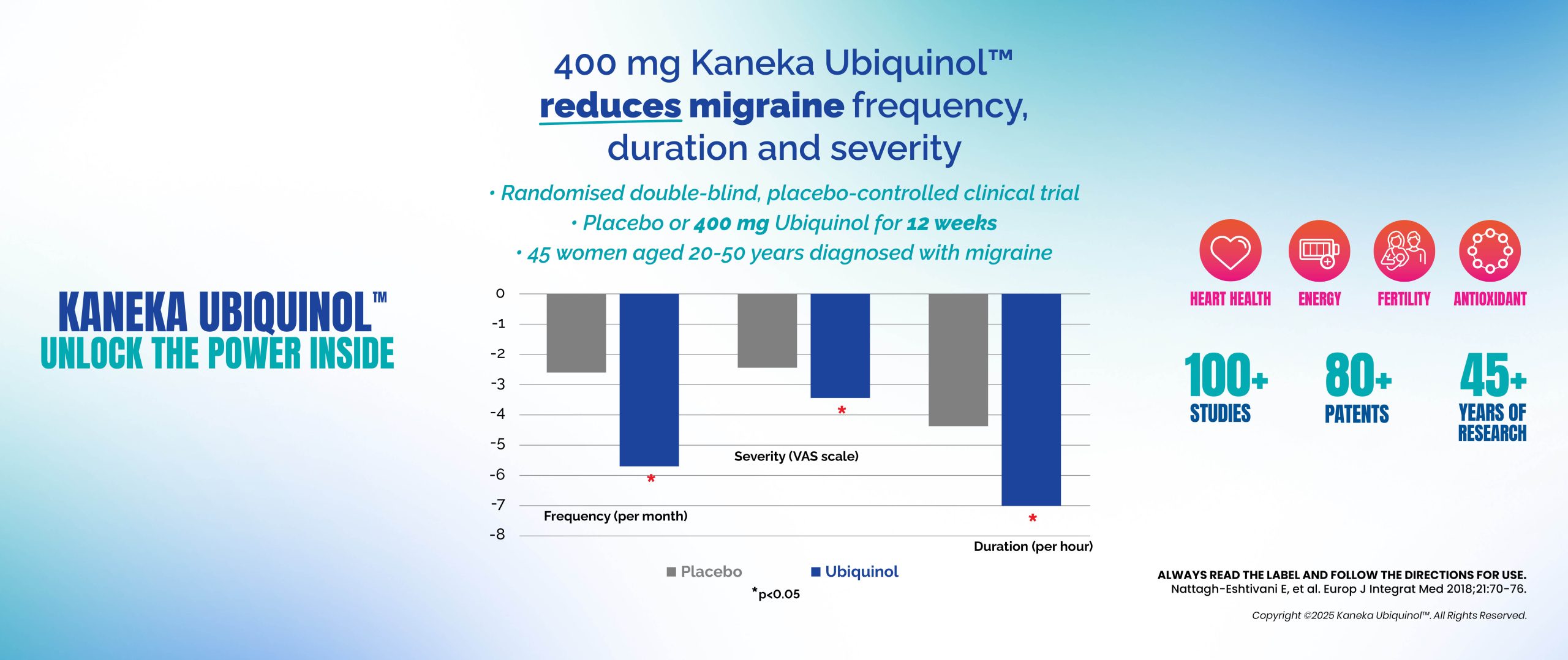
Ubiquinol: Supporting Migraine Relief Through Cellular Energy
Jan 2025Category: Antioxidants, complementary medicine, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at Functional Foods for Wellness Industry Awards and Summit, #FFWS2025
Jan 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, FFWS2025, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol Wins Prestigious Complementary Medicines Raw Material Supplier of the Year Award 2024
Dec 2024Category: Ageing, Awards, cardiovascular health, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, Lungs, Memory, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Online, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
“Powering Performance and Longevity: Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at the CMA Annual Conference 2024”
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, chronic fatigue syndrome, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, In The News, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Online, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Natural Health Product Innovation Expo 2024
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, cardiovascular health, Cholesterol, chronic fatigue syndrome, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, NHNZ, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Ubiquinol: The Overlooked Nutrient for Vegans and Vegetarians
Oct 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Cholesterol, complementary medicine, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, vitafoods, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Investigating the Application of Ubiquinol in Mitochondrial Function
Oct 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, cardiovascular health, Cholesterol, chronic fatigue syndrome, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Flu, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, long covid, Lungs, Memory, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, myalgic encephalomyelitis, Nutrition, post pandemic, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More


