
Investigating the Application of Ubiquinol in Mitochondrial Function
Oct 2024Recent Article
Research Insights into Mitochondrial Function, Key Biomarkers, and the Role of Ubiquinol
Optimising mitochondrial function remains a critical area of study, as poor mitochondrial function and metabolism are key in a variety of metabolic disorders.
Recent advancements in research have illuminated not only a selection of critical biomarkers for assessing mitochondrial health but also innovative approaches to mitigating dysfunction. Among these, Ubiquinol has emerged as a promising intervention, targeting many of the identified processes that can lead to mitochondrial damage.
🔍 Key Findings
📚 A 2024 study published in the journal Neurobiology of Disease provides new evidence on the interplay between certain metabolic biomarkers, impaired mitochondrial function, and the application of Ubiquinol. The findings highlight the critical role of monitoring the following areas for understanding and managing metabolic disturbances.
- Oxidative Stress and Mitochondria: Dysfunction in the electron transport chain (ETC) and the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) can lead to PDC deficiency and impaired mitochondria. In fact, defects in the PDC can impact approximately 5% of cases of mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders, leading to an increase in oxidative stress and metabolic challenges.
- Metabolic Biomarkers Used to Assess Mitochondrial Dysfunction:
-
- Elevations in pyruvate and lactate – With a slowed tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle due to impaired mitochondrial function, pyruvate accumulates and is diverted into alternative pathways, increasing lactate and alanine levels.
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) – This enzyme, which converts pyruvate to lactate, serving as a crucial biomarker when the mitochondria are under stress.
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) – This liver enzyme is responsible for converting pyruvate to alanine and plays a role in metabolizing glutamate to alpha-ketoglutarate, an essential TCA cycle metabolite.
- Low total or free carnitine – As a carrier of long-chain fatty acids, low levels indicate a disruption in fatty acid metabolism for several metabolic disorders.
- Imbalance of butyrate and propionate short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) – The two major SCFAs produced by the microbiome impact the citric acid cycle; variations in colonic microbiome content can disrupt mitochondrial function.
-
- Monitoring Ratios:
-
-
- Lactate to pyruvate – Used to gauge mitochondrial function and oxidative stress levels.
- Alanine to lysine – Helps in assessing the metabolic status related to mitochondrial health.
-
💡Innovative Approach: Ubiquinol for Mitochondrial Health
The study explored the benefits of Ubiquinol, where these biomarkers were found in individuals to indicate the need for further mitochondrial support. Ubiquinol plays an essential role in the ETC, enhancing mitochondrial energy production and reducing oxidative stress.
-
-
- Enhanced Cellular Energy: Ubiquinol given at 5-30mg/kg/day 1-2 times daily improves ATP production by supporting the ETC.
- Reduced Oxidative Stress: With its well-documented antioxidant properties, Ubiquinol given at 5-30mg/kg/day 1-2 times daily helps combat high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced during electron transfer, preserving mitochondrial integrity and reducing oxidative stress.
- Clinical Evidence: Ubiquinol supplementation can positively influence biomarkers associated with mitochondrial health and function, offering a promising strategy for conditions involving impaired mitochondrial processes.
-
🔬Implications: Monitoring levels of pyruvate, lactate, and alanine can provide valuable insights into assessing mitochondrial health and function. Incorporating Ubiquinol offers an innovative and evidence-based avenue for enhancing mitochondrial function and managing metabolic imbalances.
Reference: Frye RE, et al. Biomarkers of mitochondrial dysfunction in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiology of Disease 2024;197:106520.
Always read the label and follow the directions for use. Consult your healthcare professional to establish if Ubiquinol is suitable for your needs.
You can share this by:
Keep up-to-date with Ubiquinol News
Ubiquinol Headlines

Ubiquinol and Healthy Ageing: A Conversation with Dr Denis Furness on the House of Wellness Radio
Jun 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Broadcast, Energy, Fatigue, Health, healthy ageing, In The News, Mitochondrial health, Ubiquinol, wellnessRead More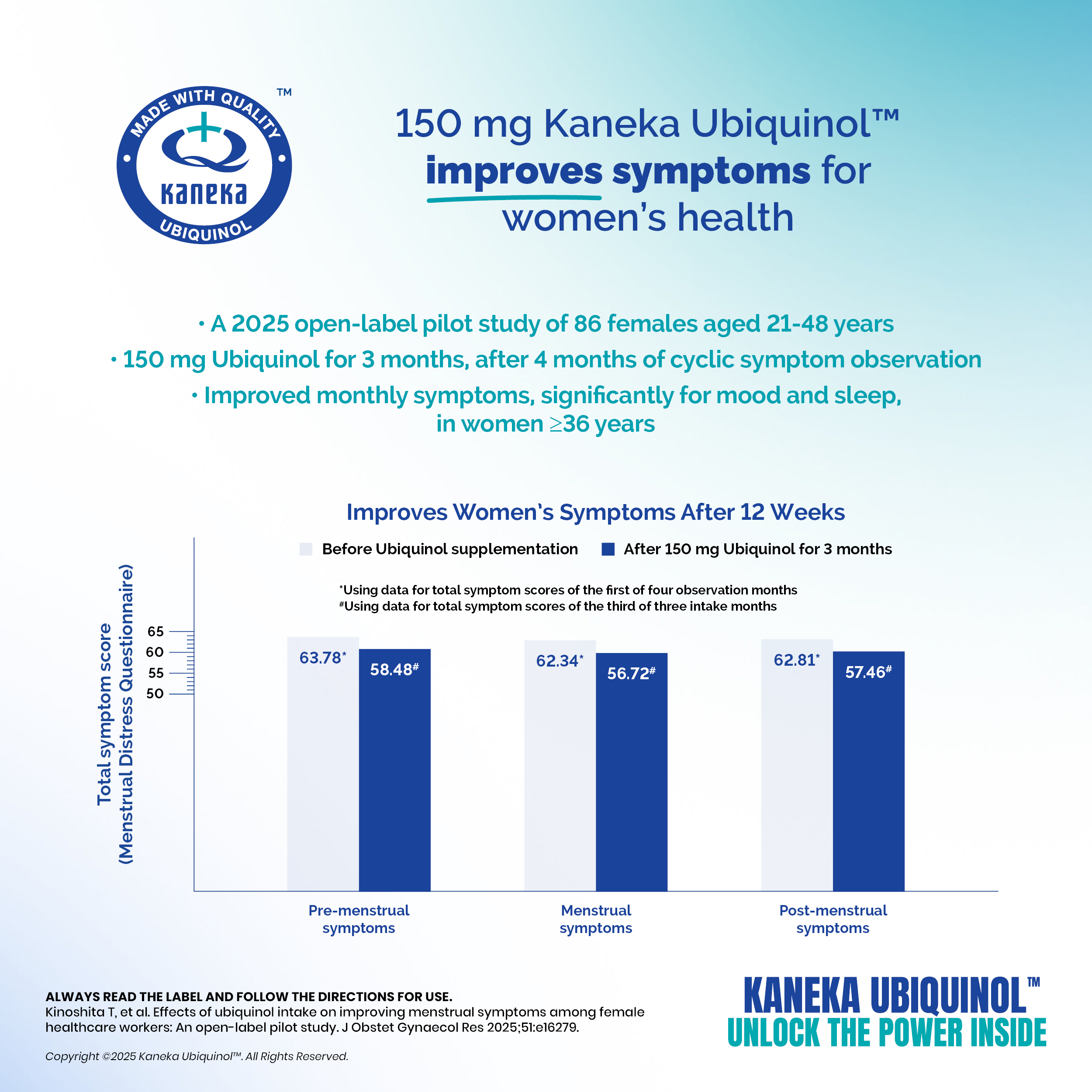
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ for Relief of Women’s Symptoms
May 2025Category: Ageing, Fertility, Menopause, Ubiquinol, wellness, Women's HealthRead More
Mitochondrial Health in Women’s Wellbeing: Key Insights from CMA Innovation Day 2025
May 2025Category: Antioxidants, Conferences, Fertility, Menopause, Ubiquinol, wellness, Women's HealthRead More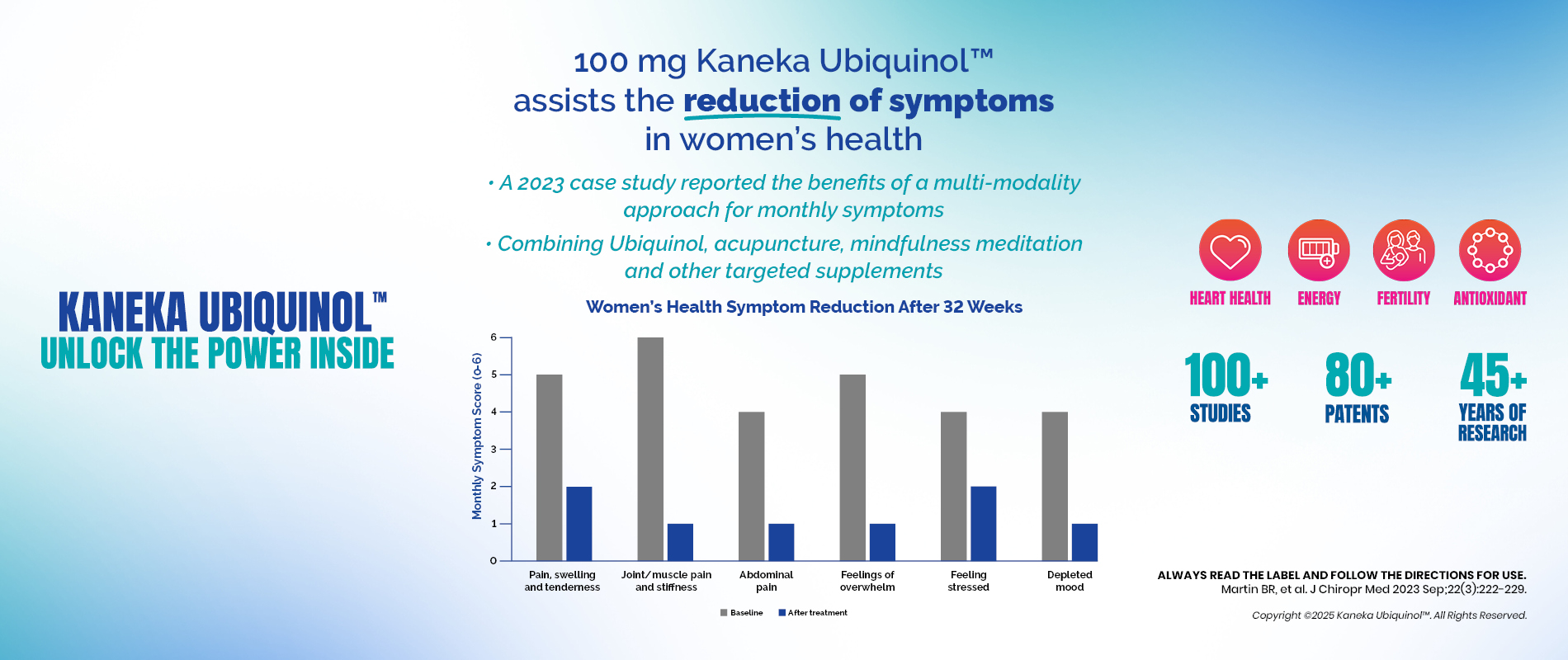
Ubiquinol for Women’s Health
Apr 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Fertility, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Ubiquinol, wellness, Women's HealthRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at APP 2025: Advancing Healthy Ageing & Longevity
Mar 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, APP, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, UbiquinolRead More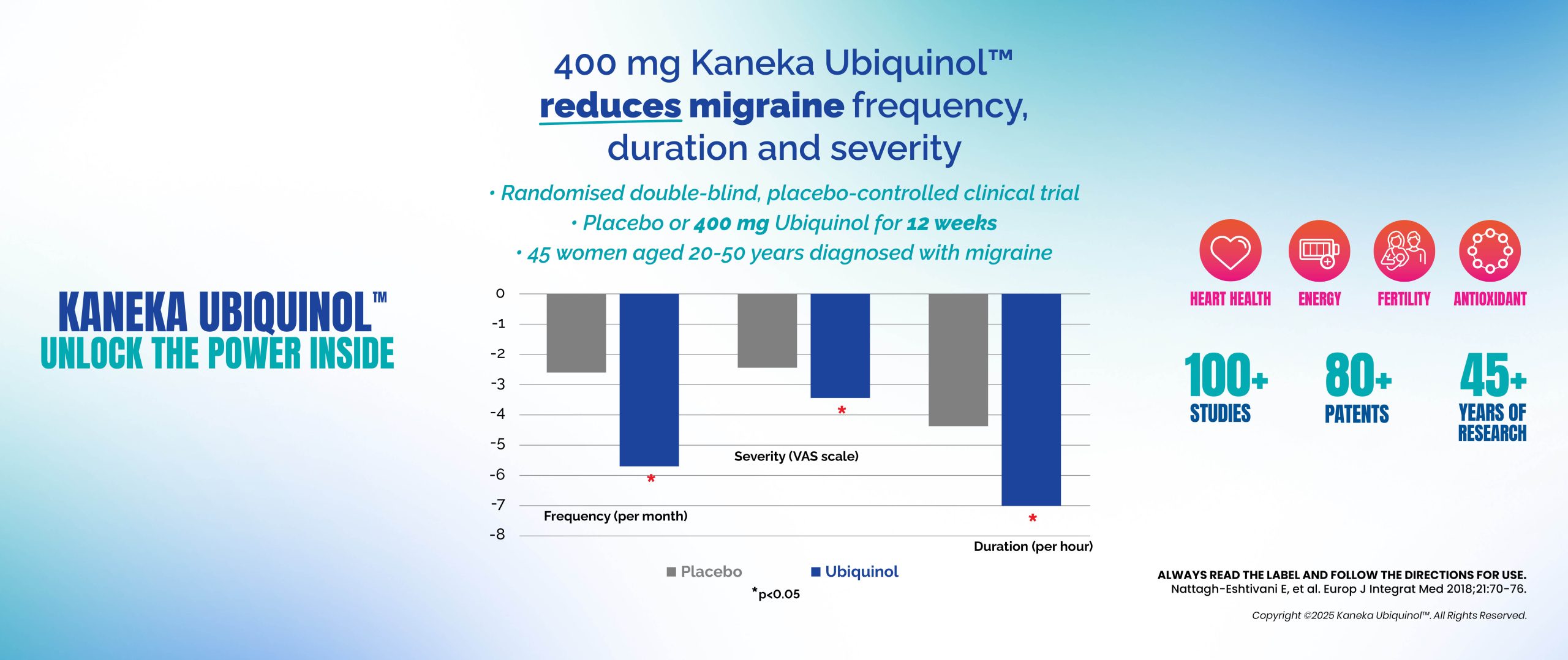
Ubiquinol: Supporting Migraine Relief Through Cellular Energy
Jan 2025Category: Antioxidants, complementary medicine, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at Functional Foods for Wellness Industry Awards and Summit, #FFWS2025
Jan 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, FFWS2025, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More




