NEW STUDY: Leading Cardiologists Recommend Ubiquinol Supplementation to Improve Heart Health
Apr 2020Recent Article
A new study has recommended Ubiquinol as a beneficial supplement to improve the health of your heart. The study, which involved leading cardiologists from Germany, Italy and Australia, found that Ubiquinol could be the key to improving the heart function of patients with chronic heart failure.
The findings of this new study published in the most recent edition of Heart, Lung and Circulation, a medical journal specialising in Cardiovascular Science and Heart Surgery_, evaluated Ubiquinol for heart health, finding “combining Ubiquinol with a Statin may benefit hypercholesterolaemic patients with chronic heart failure[1].”
The news is a relief to those in the wider community, especially as heart failure is one of the most common causes of death in western communities[1].
The cardiology experts scoured scientific papers and concluded “a strong case for considering co-administration of Ubiquinol with Statin therapy in patients with poor myocardial function.”
“Ubiquinol, the active reduced form of CoQ10, presents higher bioavailability than the oxidised form ubiquinone, and should be the preferred form,” say the researchers referring to supplementation[2]. CoQ10, also referred to as coenzyme Q10, is a critical component for metabolism and energy production in all human cells[3]. Supplementation promotes improved cardiovascular relaxation by balancing oxidative and reductive (redox) reactions, important in protecting the heart muscle from oxidative or free radical damage[4].
A commonly prescribed medication for hypercholesterolemia is known to cause some muscle damage in up to 40% of cases in some clinical trials, say the researchers, with the damage appearing to be dose-dependant. This is potentially due to the medication partially blocking endogenous CoQ10 synthesis as it inhibits a pathway. Overtime, and depending on the dose, this may lead to CoQ10 deficiency and hence potential muscular tissue damage.
With ageing there is also a reduction in the activity of enzymes responsible for converting CoQ10 to the active form, Ubiquinol. The researchers note there is a strong link to depleted plasma CoQ10 levels and the severity of some cardiovascular health issues.
Based on this preliminary evidence the researchers recommended a daily dose of 300mg of Ubiquinol to increase blood plasma levels of the important coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in patients with sub-optimal depleted levels.
The researchers conclude “Therefore we believe that the co-administration of 300mg ubiquinol with the combination eztimibe/statin should be the preferred initial therapeutic option for LDL-lowering in patients with heart failure and hypercholesterolemia, especially in those with high oxidative stress and coronary arterial disease.”
About Ubiquinol
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is found in all cell membranes and lipoproteins, existing in both reduced and oxidised states, namely Ubiquinol and Ubiquinones. Ubiquinol is the active reduced form of CoQ10. CoQ10 is critical for cellular function, providing cellular energy and as an important potent antioxidant required for every cell of the body, including heart cells_[5]. Research shows that Ubiquinol helps to maintain a healthy heart and cardiovascular system[6]_.
Because of its essential role in energy production, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress[7]_, it’s worth researching whether Ubiquinol could suit you and your lifestyle.
Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist consult your health care practitioner.
[1] 1. Combining Ubiquinol With a Statin May Benefit Hypercholesterolaemic Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. Kloer, Hans-Ulrich et al. 2, 2020 , Heart, Lung and Circulation, Vol. 29, pp. 188 – 195.
[1] https://www.heartfoundation.org.au/about-us/what-we-do/heart-disease-in-australia
[2] 1. Combining Ubiquinol With a Statin May Benefit Hypercholesterolaemic Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. Kloer, Hans-Ulrich et al. 2, 2020 , Heart, Lung and Circulation, Vol. 29, pp. 188 – 195.
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178961/
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249911/
[5] Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors. K, Rahman. 2, Clin Interv Aging, Vol. 2, pp. 219-236.
[6] Coenzyme Q10 redox state predicts the concentration of c-reactive protein in a large caucasian cohort. Fischer, A, et al. 3, 2016, Biofactors, Vol. 42, pp. 268-76.
[7] https://www.kanekanutrients.com/what-ubiquinol-0
You can share this by:
Keep up-to-date with Ubiquinol News
Ubiquinol Headlines
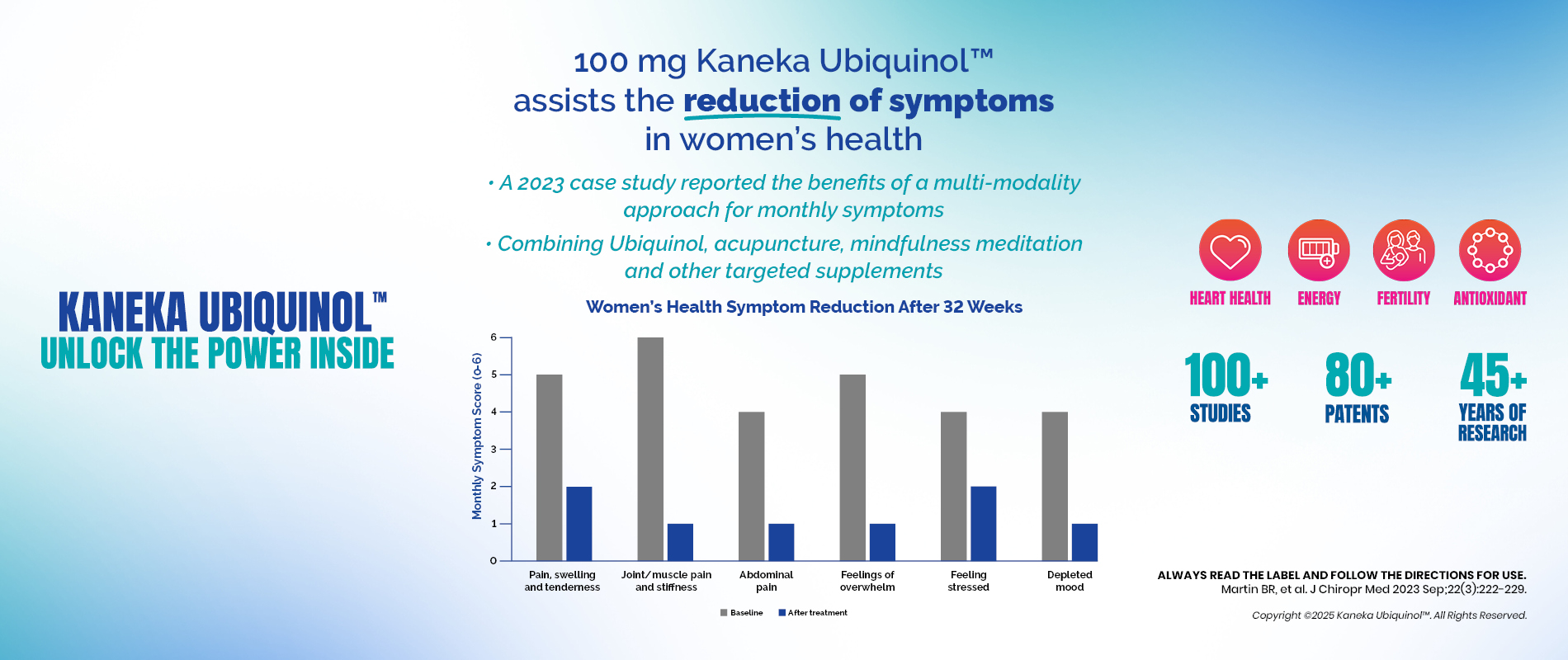
Ubiquinol for Women’s Health
Apr 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Fertility, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Ubiquinol, wellness, Women's HealthRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at APP 2025: Advancing Healthy Ageing & Longevity
Mar 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, APP, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, UbiquinolRead More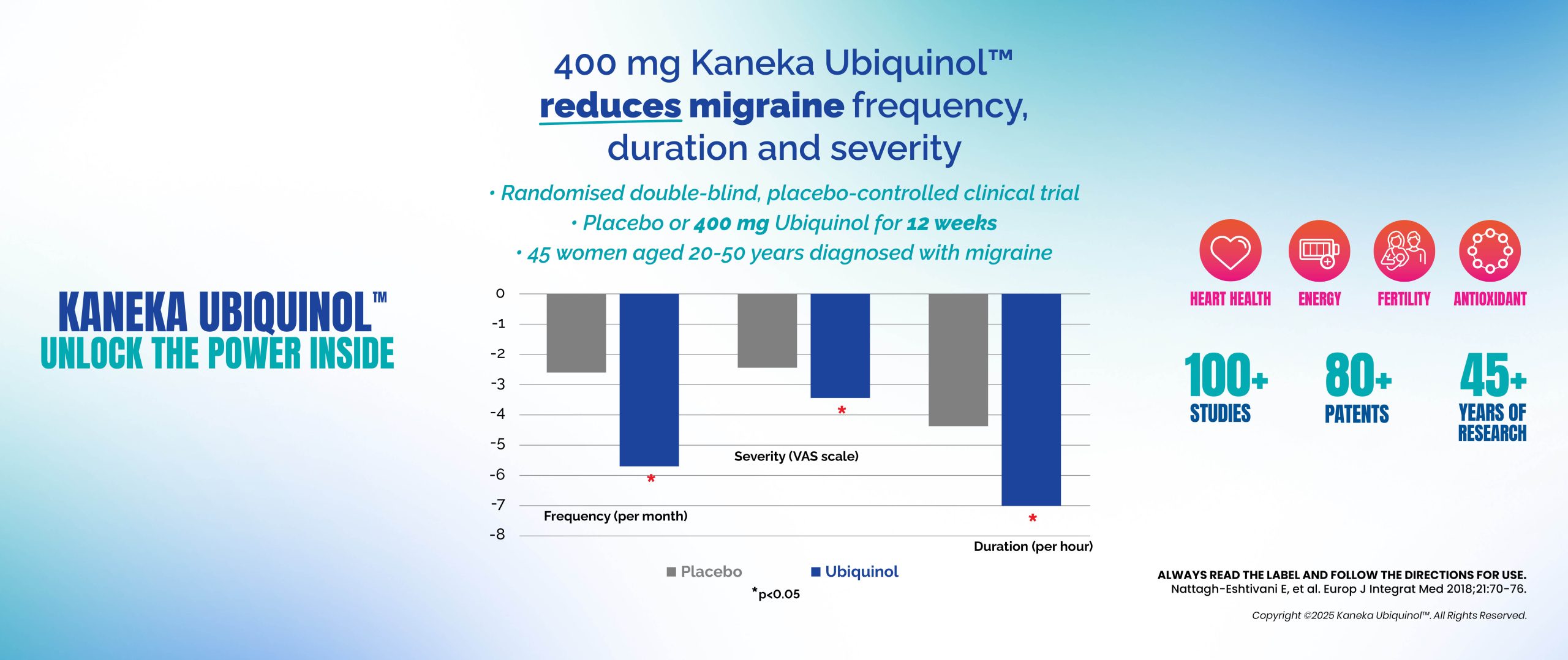
Ubiquinol: Supporting Migraine Relief Through Cellular Energy
Jan 2025Category: Antioxidants, complementary medicine, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at Functional Foods for Wellness Industry Awards and Summit, #FFWS2025
Jan 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, FFWS2025, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol Wins Prestigious Complementary Medicines Raw Material Supplier of the Year Award 2024
Dec 2024Category: Ageing, Awards, cardiovascular health, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, Lungs, Memory, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Online, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
“Powering Performance and Longevity: Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at the CMA Annual Conference 2024”
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, chronic fatigue syndrome, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, In The News, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Online, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Natural Health Product Innovation Expo 2024
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, cardiovascular health, Cholesterol, chronic fatigue syndrome, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, NHNZ, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More



