Mitochondrial Energy and Ubiquinol
Jul 2019Recent Article
We all need energy to get us through the day. However, understanding how we produce energy is also important in knowing how to go about supporting healthy and sustainable energy production.
A vital component of energy production is Mitochondrial Energy, which is derived from the food and nutrients we eat.
Here is a breakdown of how this process works and how you can support optimal energy levels through the supplementation of Ubiquinol.

What is Mitochondrial Energy?
Mitochondrial energy is created by the food we digest, converting it into energy for the rest of the cell to utilise and playing an essential role in the metabolising of energy[i]. The production of mitochondrial energy transforms into ATP, which is the energy the body requires for physical output[ii].
However, the mitochondria does more than simply produce energy, it also plays an important role in generating the chemicals your body requires to save and recycle waste as well as break down waste products, reducing harmfulness.[iii]
How does Mitochondrial Energy work?
In better understanding mitochondrial energy production, it may be simpler to think of it as a secondary digestive system. Taking in nutrients, breaking them down and keeping the cell energised—this biochemical process is also known as cellular respiration[iv]. Our muscles require the largest amount of mitochondria in our body and therefore, the highest count of mitochondria can be found in our muscles[v].
How does Ubiquinol Support the Mitochondria?
Even though the mitochondria is commonly referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, it still needs the right nutrients in order to convert the food we put into our body into energy[vi]. If the mitochondria is not working effectively, it is likely a consequence of what we are fuelling our bodies with. A western lifestyle does not always provide a nutrient-filled diet, however, through healthy eating and regularly physical activity, we are supporting effective mitochondrial energy production.[vii]
Another way to support healthy mitochondrial energy production is through Ubiquinol supplementation. Ubiquinol is already naturally produced within our bodies, however as we age, our Ubiquinol levels decline, therefore making it harder to stay energised and may cause oxidative damage. In addition, the stresses and strains of our busy lifestyle also contribute to the reduction in CoQ10 levels. The mitochondria are especially susceptible to nutrient deficiencies, environmental toxins, and oxidative damage[viii]. Through Ubiquinol supplementation you can boost your CoQ10 levels and help power the mitochondria.
[i] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005272810000058
[ii] https://bscb.org/learning-resources/softcell-e-learning/mitochondrion-much-more-than-an-energy-converter/
[iii] https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/11/131129101803.htm
[iv] https://www.elysiumhealth.com/en-us/knowledge/science-101/what-do-the-mitochondria-do
[v] https://www.mpg.de/11997935/muscle-cells-mitochondria
[vii] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4684129/
[viii] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4684129/
You can share this by:
Keep up-to-date with Ubiquinol News
Ubiquinol Headlines
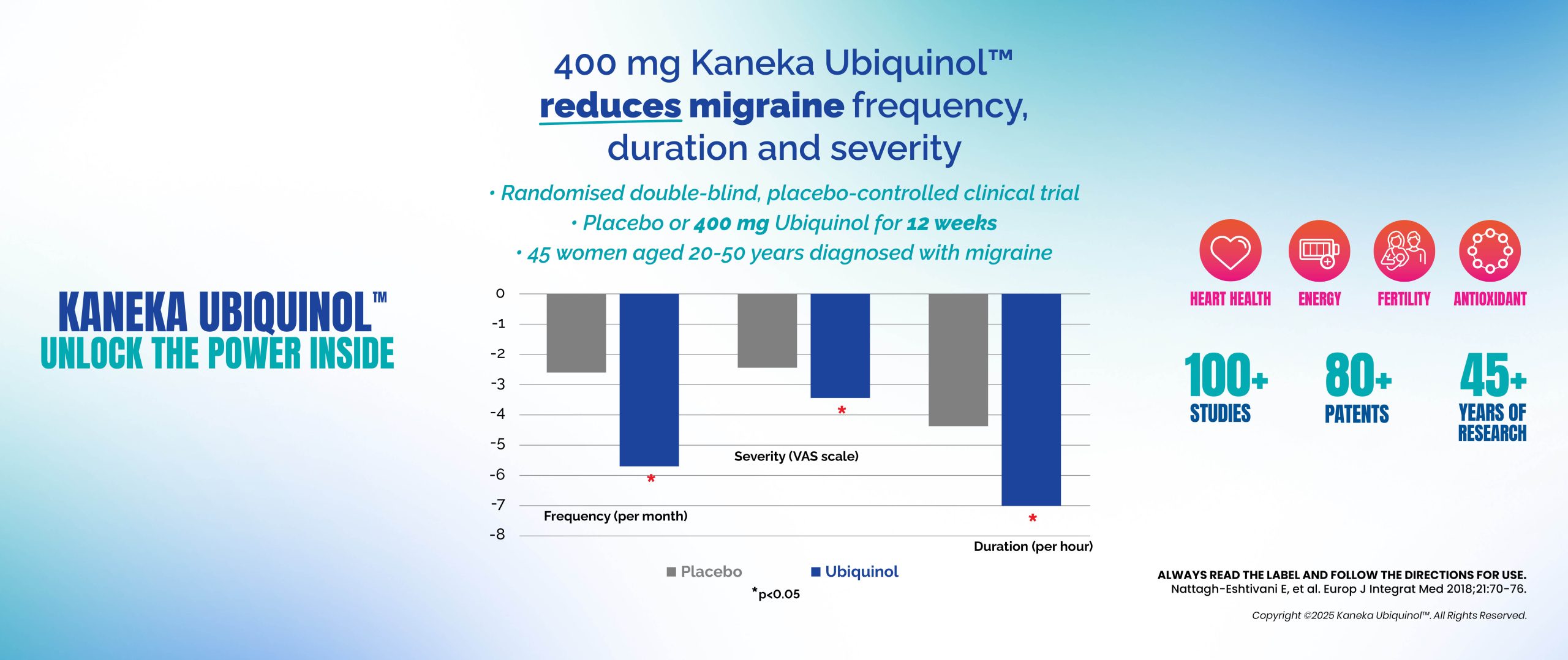
Ubiquinol: Supporting Migraine Relief Through Cellular Energy
Jan 2025Category: Antioxidants, complementary medicine, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at Functional Foods for Wellness Industry Awards and Summit, #FFWS2025
Jan 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, FFWS2025, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol Wins Prestigious Complementary Medicines Raw Material Supplier of the Year Award 2024
Dec 2024Category: Ageing, Awards, cardiovascular health, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, Lungs, Memory, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Online, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
“Powering Performance and Longevity: Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at the CMA Annual Conference 2024”
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, chronic fatigue syndrome, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, In The News, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Online, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Natural Health Product Innovation Expo 2024
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, cardiovascular health, Cholesterol, chronic fatigue syndrome, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, NHNZ, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Ubiquinol: The Overlooked Nutrient for Vegans and Vegetarians
Oct 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Cholesterol, complementary medicine, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, vitafoods, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Investigating the Application of Ubiquinol in Mitochondrial Function
Oct 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, cardiovascular health, Cholesterol, chronic fatigue syndrome, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Flu, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, long covid, Lungs, Memory, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, myalgic encephalomyelitis, Nutrition, post pandemic, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More


