
When Should you Supplement with Ubiquinol?
Apr 2022Recent Article
Situations Best Suited for Ubiquinol Supplementation
With busy lives, it is only normal for our energy levels to dip. Fortunately, there are some natural ways in which we can not only support our energy levels, but also our overall wellbeing.
Ubiquinol, the active and more easily absorbed form of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a naturally occurring antioxidant responsible for providing our cells with energy.[1] It helps protect against free radicals and supports the body as it ages.[2]
Our bodies convert conventional CoQ10 (ubiquinone) into ubiquinol before it can be used to create cellular energy. It is therefore a critical component of energy production for every cell of the body. It is concentrated in the organs that require the most energy, such as the heart, liver, muscles and kidneys.[2] While ubiquinol can be absorbed into the body through foods, such as meat, fish and wholegrains, the body’s significant requirements mean that supplementation through food is often inadequate.[2]
So when do we need ubiquinol supplementation?
If you are feeling fatigued
Many factors in your everyday life may be contributing to feelings of sluggishness and lethargy. If you are relying on caffeine and sugar to get through the day, Ubiquinol supplements may provide a natural energy boost and keep you feeling energised for longer. When your energy production levels are low, your body’s natural energy is compromised, hence giving your mind and body a chance to rest both during the day and at night is crucial in helping restore energy levels and keep you from feeling fatigued.[3]
If you’re over the age of 30
As we age, our natural levels of Ubiquinol tend to decline, making it harder to function at our prime, especially when faced with oxidative stress and the impact of free radicals.[2] Ubiquinol supplements, on top of a nutrient dense and super-food rich diet, may play an important role in keeping you energised and healthy for longer. Proteins such as green vegetables and lean meats, as well as legumes are an easy addition to meals to make sure you are giving your body the fuel it needs.
If you want to support your heart health
Ubiquinol has been scientifically linked to maintaining a healthy heart by providing and maintaining the levels of cellular energy needed to ensure the heart is pumping efficiently. Ubiquinol also helps maintain healthy levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein also known as bad cholesterol). Increased LDL is linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, and atherosclerosis.[4]
If you are trying to conceive
One of the key factors in egg quality is the health of the mitochondria.[5] Mitochondria are essential for supporting cellular energy production (which in this instance is the cells in the egg) as they assist in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The active form of CoQ10, ubiquinol, provides the cells (in this instance the egg cell as well as the sperm cells) with enough energy to make sure that fertilisation occurs successfully.
Mitochondria are transferred to the embryo by the mother. Sperm only bring enough mitochondria to reach the egg for fertilisation. Once an egg is fertilised, the mother’s mitochondria become the blueprint for the baby’s mitochondria.[6]
Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist consult your healthcare professional.
References:
[1] Ernster L, Forsmark-Andre P. Ubiquinol: An Endogenous Antioxidant In Aerobic Organisms. The Clinical Investigator 1993;71(S8).
[2] Saini R. Coenzyme Q10: The essential nutrient. J Pharm Bioalllied Sci 2011;3(3):466-467.
[3] Bergouignan A, et al. (2016). Effect of frequent interruptions of prolonged sitting on self-perceived levels of energy, mood, food cravings and cognitive function. Internat J Behavioural Nutr Physical Activity 2016;13(113).
[4] Kanonidou C. Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein: Analytical Review. Clinica Chimica Acta 2021;520(2021):172-178.
[5] Xu Y, et al. Pretreatment with coenzyme Q10 improves ovarian response and embryo quality in low-prognosis young women with decreased ovarian reserve: a randomized controlled trial. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 2018;16(1).
[6] Zhou Q, et al. Mitochondrial endonuclease G mediates breakdown of paternal mitochondria upon fertility. Science 2016;353(6297):394-399.
You can share this by:
Keep up-to-date with Ubiquinol News
Ubiquinol Headlines
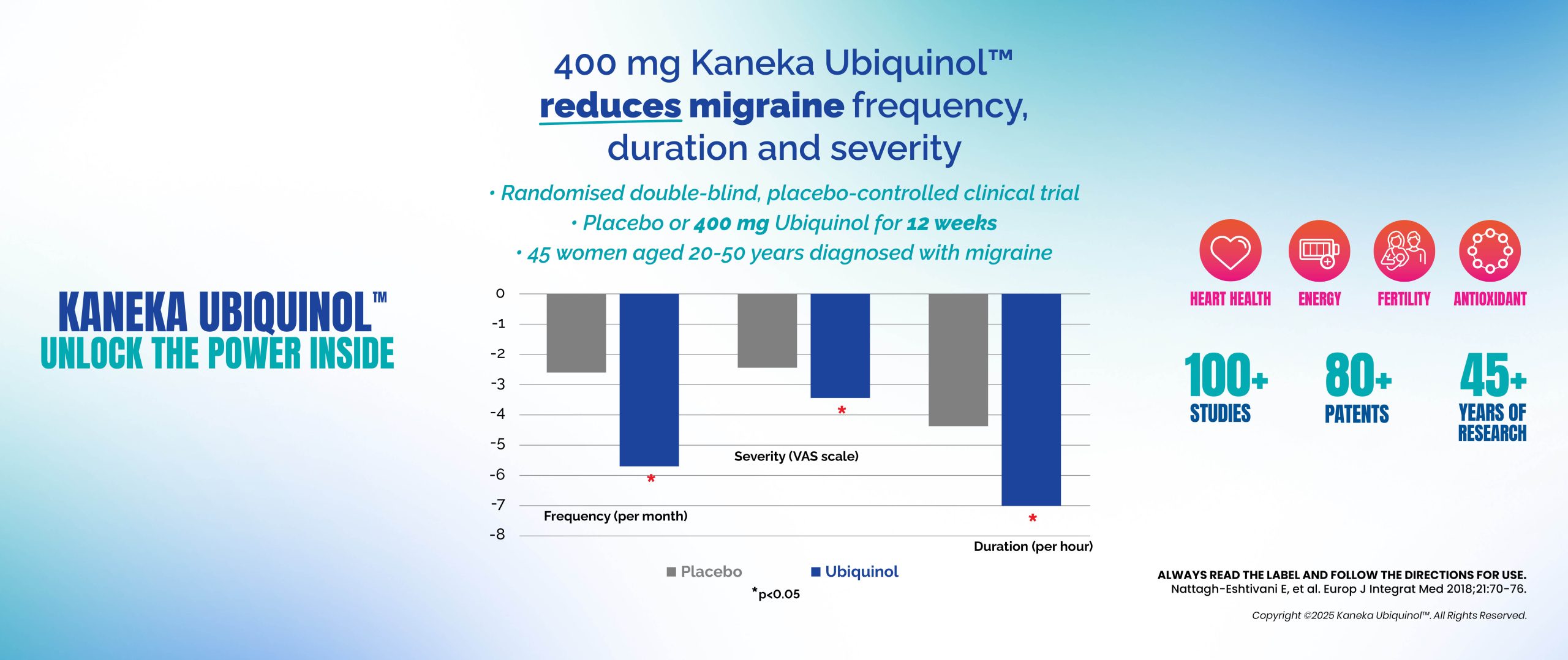
Ubiquinol: Supporting Migraine Relief Through Cellular Energy
Jan 2025Category: Antioxidants, complementary medicine, Energy, Fatigue, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at Functional Foods for Wellness Industry Awards and Summit, #FFWS2025
Jan 2025Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, Conference, Conferences, Energy, Fatigue, FFWS2025, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Kaneka Ubiquinol Wins Prestigious Complementary Medicines Raw Material Supplier of the Year Award 2024
Dec 2024Category: Ageing, Awards, cardiovascular health, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, Lungs, Memory, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Online, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
“Powering Performance and Longevity: Kaneka Ubiquinol™ at the CMA Annual Conference 2024”
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Awards, cardiovascular health, chronic fatigue syndrome, complementary medicine, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, In The News, Kaneka, Mitochondrial health, Online, Ubiquinol, VitaminsRead More
Natural Health Product Innovation Expo 2024
Nov 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, cardiovascular health, Cholesterol, chronic fatigue syndrome, Conference, Conferences, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Kaneka, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, NHNZ, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Ubiquinol: The Overlooked Nutrient for Vegans and Vegetarians
Oct 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, Cholesterol, complementary medicine, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fitness, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Mitochondrial health, Nutrition, Stress, Ubiquinol, vitafoods, Vitamins, wellnessRead More
Investigating the Application of Ubiquinol in Mitochondrial Function
Oct 2024Category: Ageing, Antioxidants, cardiovascular health, Cholesterol, chronic fatigue syndrome, Endurance, Energy, Fatigue, Fertility, Fitness, Flu, Health, Health Industry, healthy ageing, Heart, Immunity, In The News, Kaneka, long covid, Lungs, Memory, Menopause, Mitochondrial health, myalgic encephalomyelitis, Nutrition, post pandemic, Stress, Ubiquinol, Vitamins, wellnessRead More


